Uncertainties are inevitable when addressing a customer's need or solving a problem. If untested, these uncertainties can significantly risk your product's success. This article explores these uncertainties and their associated risks and provides a logical approach to testing methods. You can confidently navigate product development complexities by understanding and addressing these uncertainties.

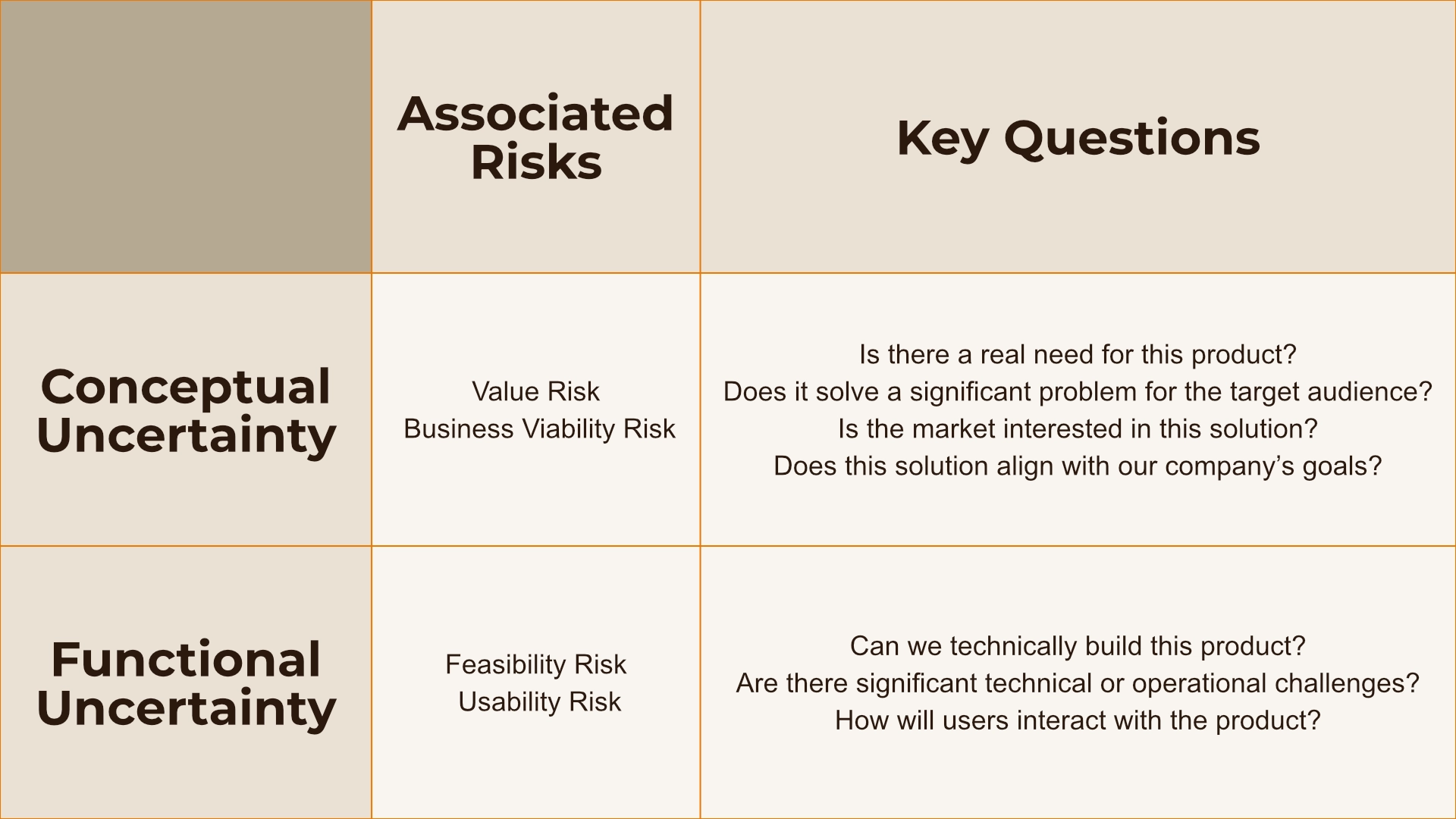
The initial focus when developing a product is on its viability. You need to determine if the product addresses a real need, solves a significant problem for your target audience, interests the market, and aligns with your company’s goals. All your questions and doubts in this phase fall under Conceptual Uncertainty.
As you gather feedback and validate the concept, another uncertainty emerges: Can you build the product as envisioned? This involves assessing technical feasibility, operational challenges, and user interactions. Every uncertainty here is related to the Functional Uncertainty.
In the early stage, you concentrate on Conceptual Uncertainty, validating your idea. Once this is under control, you address Functional Uncertainty, ensuring the product works as intended and offers a good user experience. What are you risking if you don't address these uncertainties?
Marty Cagan addresses the most intuitive risks. He identified four primary risks that every product faces:
Let's connect these risks to the uncertainties we feel during product development:
It is time to act now that we understand the uncertainties and risks we must mitigate. These uncertainties are present throughout your product development process, so you must test continuously while moving from conceptual to functional uncertainty to launch the product confidently.
Let's explore how to test these uncertainties and how to prevent these risks during your development process. I divided this into three arbitrary stages.
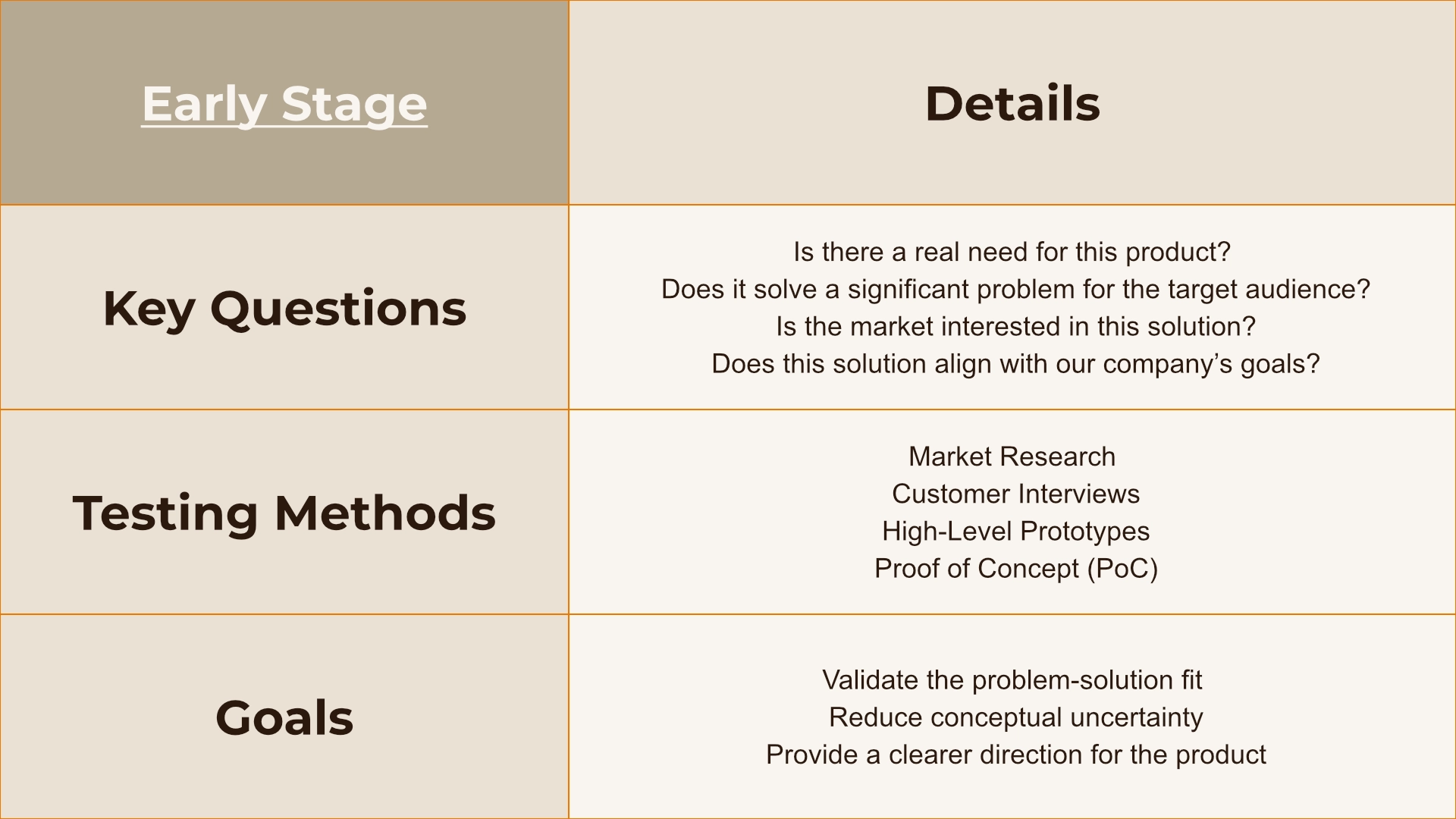
In the early stage of product development, the focus is on addressing Conceptual Uncertainty. This involves determining whether your product idea is viable and solves a significant problem for your target audience. Gathering extensive feedback is crucial to validate your concept and ensure a real market need.
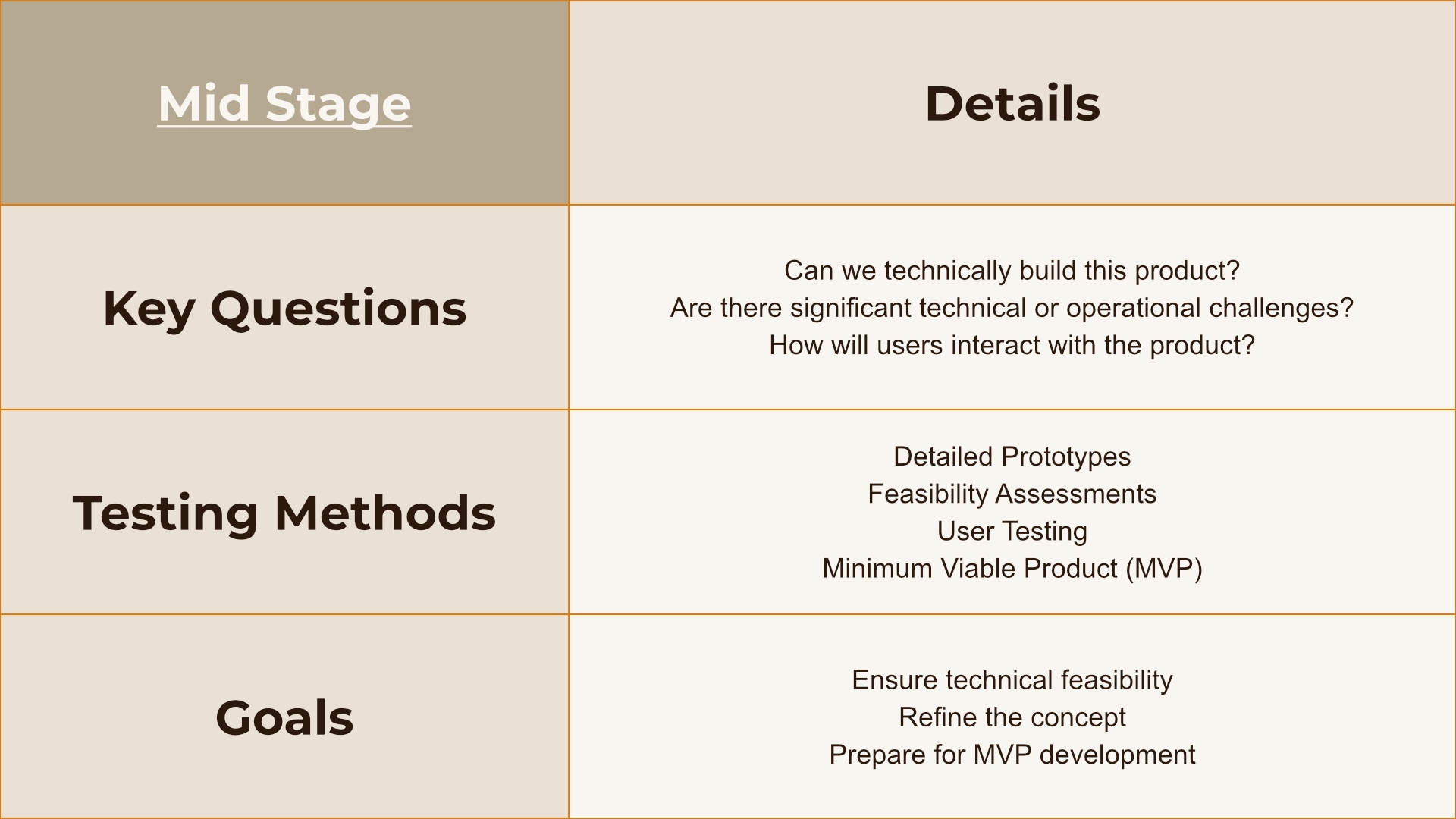
In the mid-stage, the focus shifts more towards Functional Uncertainty. This stage involves evaluating the product's technical feasibility and understanding user interactions. It requires assessing operational challenges and refining user interactions through detailed testing.
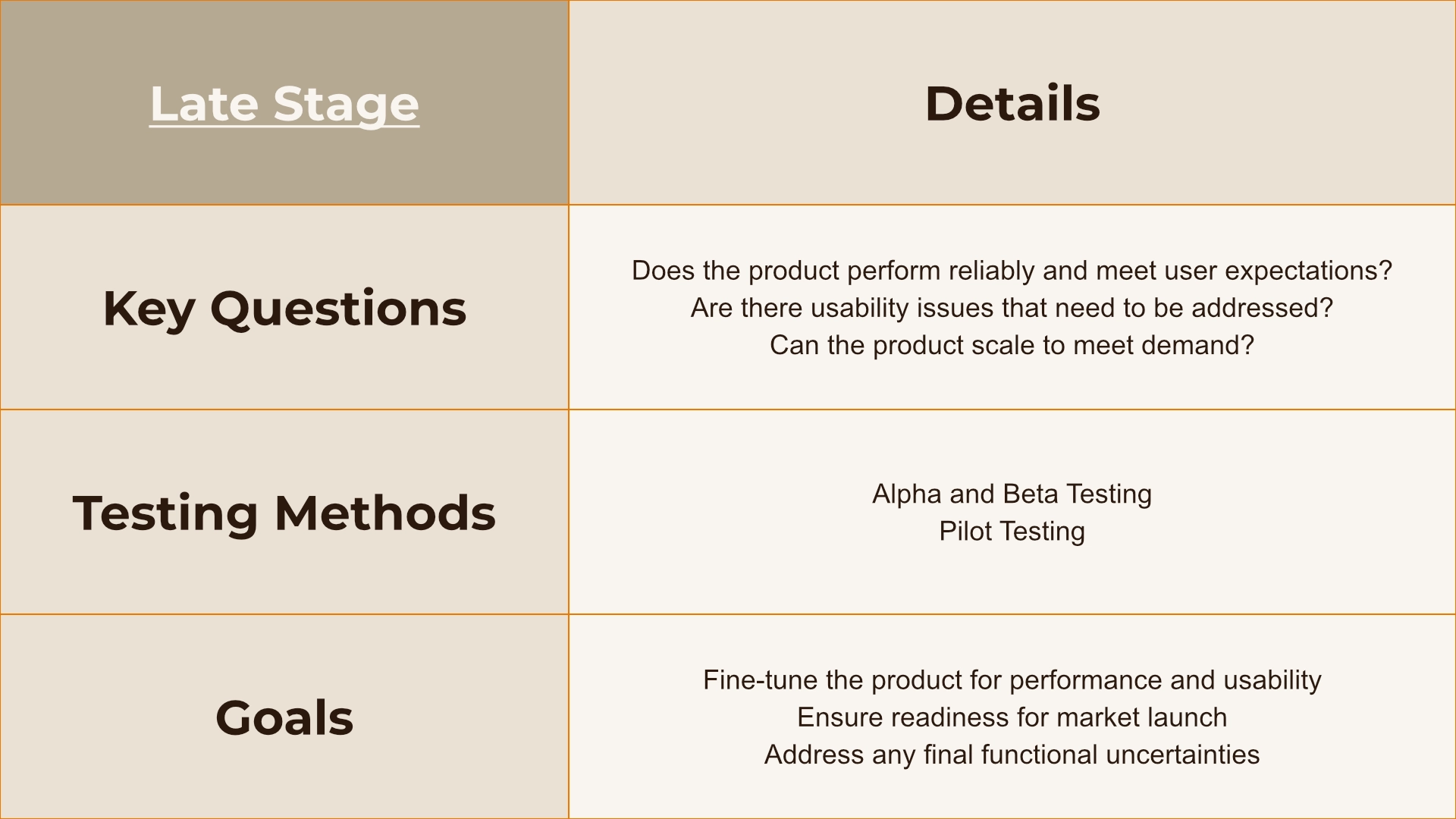
In the late stage, the focus is almost entirely on Functional Uncertainty. The goal is to ensure the product performs reliably, meets user expectations, and can scale to meet demand. This involves extensive testing and iteration to fine-tune the product.
If you bring both uncertainties together with the most common testing methods, you get this overview.
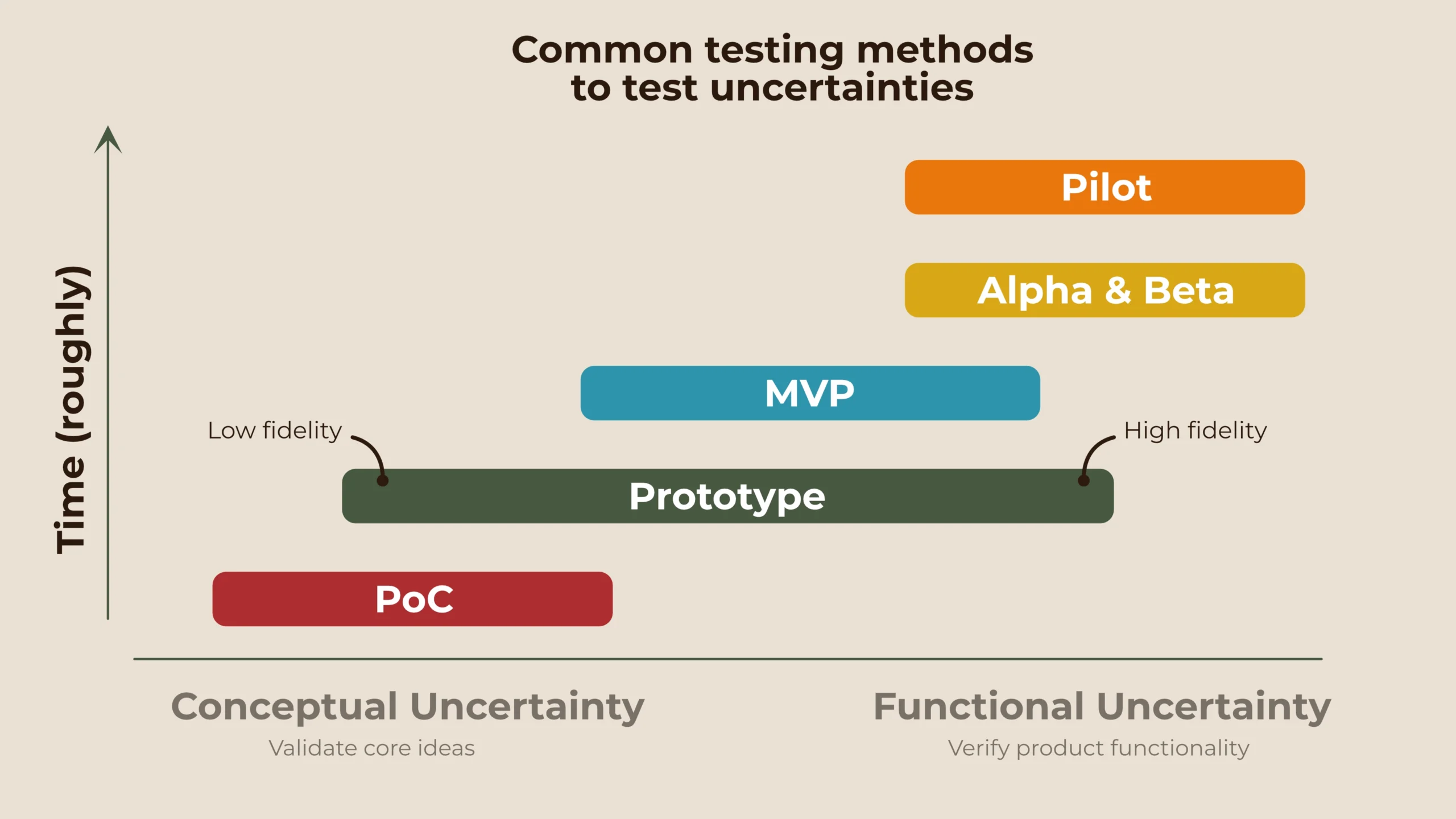
The goal is not to follow this or any article to the letter. It’s about understanding the mindset of uncertainty, identifying risks, and testing them. You and your team can adapt and succeed by grasping these building blocks. Here is a list of practical tips.
Understanding and Explaining Uncertainty
Team Integration and Ownership
Culture and Mindset
Tools and Methodologies
Flexibility and Adaptability
Testing is crucial because it helps identify and mitigate uncertainties and risks. It ensures the product is viable, feasible, and user-friendly before launch.
Conceptual uncertainty can be addressed through market research, customer interviews, high-level prototypes, and proof of concept (PoC) to validate the problem-solution fit and reduce uncertainty.
Functional uncertainty can be addressed through detailed prototypes, feasibility assessments, user testing, and developing a minimum viable product (MVP) to ensure technical feasibility and refine the concept.